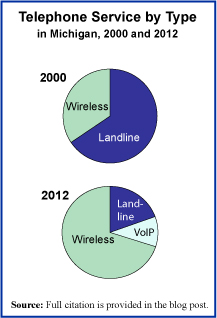
The past decade has been one of great changes in the telephone service landscape. As investment has been made in the wireless infrastructure, cell phone coverage has become much more reliable. With growing reliability of cell phones has come the option for many to do away with one’s landline phone service. The pie chart on the right shows this clearly. In the State of Michigan, the decline of landline accounts and the rise of wireless accounts has been significant since the turn of the century. For the year 2012, the graph includes a count of the users of a system called VoIP, which stands for Voice over Internet Protocol and is a telephone-like service offered to those with access to high-speed Internet connections.
There is now legislation pending in the State of Michigan to allow landline telephone service providers to begin discontinuing service to customers, after a 90-day notice, starting in 2017. This legislation would, in essence, do away with the legal right to have access to landline phone service at almost any address in the United States, a right that dates back to the early 1910s and was updated most recently in the FCC Telecommunications Act of 1996.
Michigan would not be the first state to pass such legislation. Similar laws have already passed in other states like Texas, Florida, and North Carolina. As the landscape for telephone service changes, one can not help but worry about those in areas not well covered by alternate phone service options. While wireless coverage has improved significantly over the years it is not yet near universally accessible and many people still depend upon landline service for dependable telephone connectivity.
Today’s market size is the number of phone service accounts, regardless of type—landline, wireless cell service, and/or VoIP—in the State of Michigan in 2000 and 2012. Worth noting is the population of the State in Michigan in those two years; 9.94 million and 9.88 million respectively (yes, Michigan did actually lose population over this period). Thus, the number of telephone service accounts per capita has risen over this period from 1.03 to 1.35.
Geographic reference: Michigan
Year: 2000 and 2012
Market size: 10.2 million (66% of which were landline accounts) and 13.3 million (20% landline accounts) respectively
Sources: (1) Kathleen Gray, “Still Have a Landline? Proposed Michigan Legislation Could Spell The End by 2017,” Detroit Free Press, November 18, 2013, available online here. (2) David Cay Johnson, “Phone Service for All, No Matter What Kind,” Reuters, March 28, 2012, available online here. (3) “State & County QuickFacts—Michigan,” an extract of Census Bureau data on population statistics made available on the Census web site here.
Original source: U.S. Federal Communications Commission and the U.S. Census Bureau
Posted on November 18, 2013

